5 Things Women Should Know Before Getting a Catheter - Medical Observations
Women considering a urinary catheter should be informed about several important aspects before making a decision. A doctor outlines five key points: the specific purpose of urinary catheters, potential concerns regarding health and comfort, the process of catheter insertion, the importance of proper maintenance, and aftercare recommendations to ensure a positive experience. Understanding these factors can help in making an informed choice about catheter use.
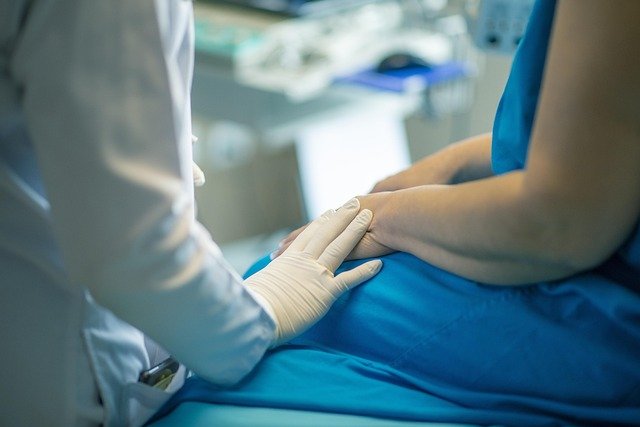
Urinary catheterization is a common medical procedure that serves various therapeutic purposes for women across different age groups and health conditions. Medical professionals use catheters to drain urine from the bladder when normal urination becomes difficult or impossible, during certain surgical procedures, or to monitor urine output in critically ill patients.
Understanding the Purpose and Usage of Urinary Catheters for Women
Urinary catheters serve multiple medical functions that healthcare providers carefully consider before recommending their use. The primary purpose involves draining urine from the bladder when natural urination is compromised due to medical conditions, surgical procedures, or temporary health issues. Women may require catheterization during childbirth complications, pelvic surgeries, or when experiencing urinary retention caused by medications, infections, or neurological conditions.
Short-term catheter use typically occurs during hospital stays for surgical procedures, particularly those involving the pelvic region, abdomen, or when patients receive general anesthesia for extended periods. Long-term catheterization becomes necessary for women with chronic conditions such as spinal cord injuries, severe bladder dysfunction, or progressive neurological disorders that affect bladder control.
The decision to use a catheter always involves weighing medical benefits against potential risks, with healthcare providers selecting the most appropriate type and duration based on individual patient needs and circumstances.
Common Concerns and Health Considerations Regarding Catheter Use
Women facing catheterization often experience anxiety about discomfort, infection risks, and lifestyle impacts. Understanding these concerns helps prepare for the experience and enables better communication with healthcare teams about expectations and management strategies.
Infection prevention represents the most critical health consideration during catheter use. Urinary tract infections occur more frequently with catheter placement, making proper hygiene and sterile insertion techniques essential. Healthcare providers implement strict protocols to minimize infection risks, including using sterile equipment, maintaining closed drainage systems, and monitoring for early signs of complications.
Discomfort during insertion and while wearing a catheter varies among individuals. Most women experience mild discomfort during the initial insertion process, which typically subsides quickly. Some may feel bladder spasms or pressure sensations while the catheter remains in place, particularly during the first few hours after insertion.
Mobility concerns often worry women about catheter placement affecting daily activities. Modern catheter systems include secure attachment methods and drainage bags that allow reasonable movement while maintaining proper positioning and preventing accidental removal.
Aftercare and Maintenance Tips for Catheter Users
Proper catheter maintenance significantly reduces complication risks and improves comfort during use. Women with catheters must follow specific hygiene protocols and monitoring guidelines to ensure safe and effective treatment outcomes.
Daily cleaning around the catheter insertion site using mild soap and water helps prevent bacterial buildup and reduces infection risks. Healthcare providers typically recommend cleaning the area twice daily and after bowel movements, always washing hands thoroughly before and after touching the catheter or drainage system.
Drainage bag management requires attention to positioning, emptying schedules, and connection security. Keeping the drainage bag below bladder level prevents urine backflow, while regular emptying prevents overfilling and maintains proper drainage function. Most healthcare teams recommend emptying drainage bags when they reach half to two-thirds capacity.
Fluid intake monitoring becomes important during catheter use, as adequate hydration helps flush bacteria from the urinary system and maintains healthy urine flow. Unless medical conditions require fluid restrictions, women should maintain normal hydration levels while avoiding excessive fluid intake that could overwhelm drainage systems.
Signs requiring immediate medical attention include fever, chills, severe abdominal pain, blood in urine, catheter blockage, or accidental removal. Healthcare providers typically provide detailed instructions about when to contact medical teams and what symptoms warrant emergency care.
Regular follow-up appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor catheter function, assess healing progress, and determine appropriate removal timing. These visits also provide opportunities to address concerns, adjust care plans, and ensure optimal outcomes throughout the treatment period.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




