Automotive Mechanic Training Insights for Residents of the UK
Residents of the United Kingdom who are proficient in English may be interested in the process of automotive mechanic training. This training encompasses a range of skills and knowledge necessary for diagnosing and repairing vehicles. It provides a structured approach to understanding automotive systems, tools, and techniques, helping individuals gain essential competencies in the field.

Understanding the Fundamentals of Automotive Mechanic Training in the UK
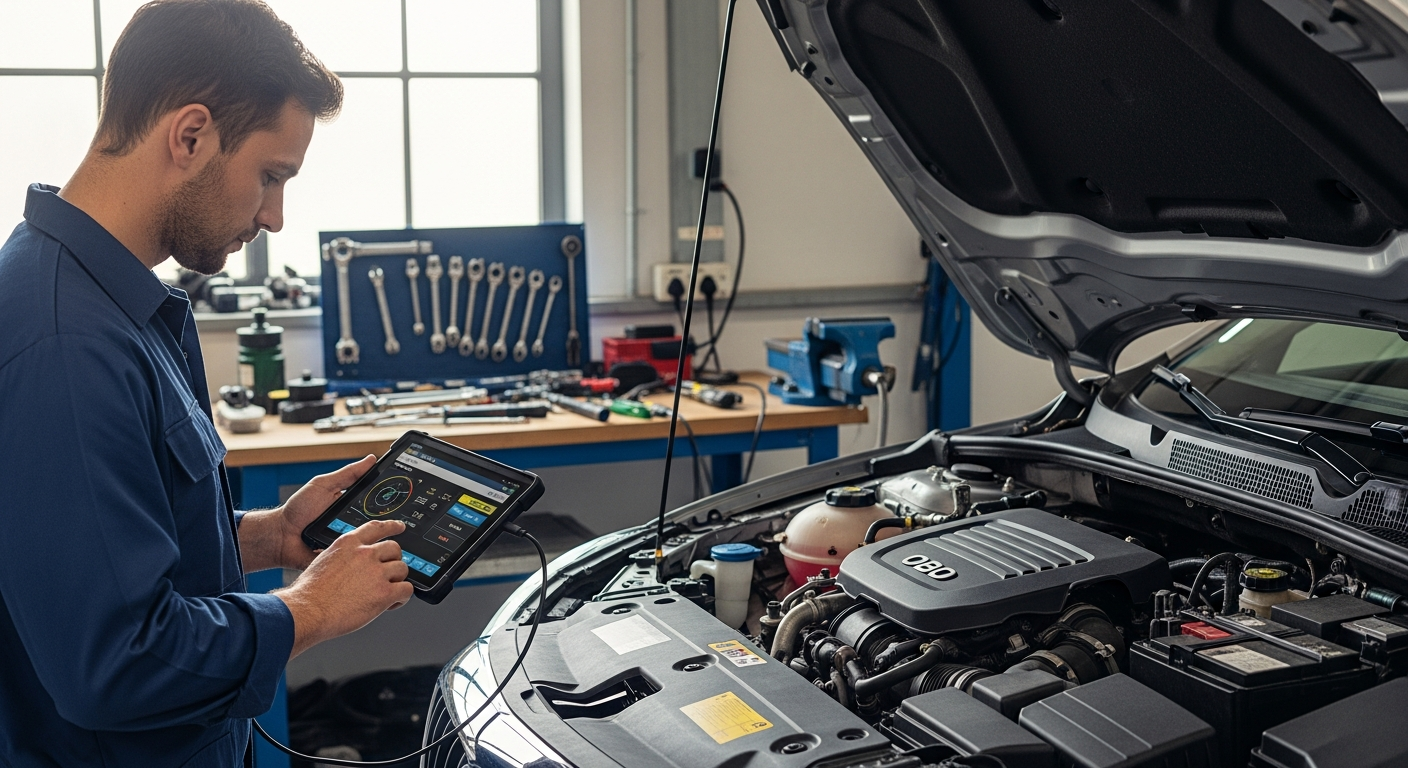
Automotive mechanic training in the UK follows a structured approach that combines classroom instruction with practical workshop experience. Most programs begin with foundational knowledge covering engine systems, electrical components, and basic vehicle operations. Students learn about different vehicle types, from traditional petrol and diesel engines to hybrid and electric vehicles. The curriculum typically includes safety protocols, tool usage, and industry regulations that govern automotive repair work. Training providers ensure students understand both mechanical principles and modern diagnostic techniques essential for contemporary vehicle servicing.
Key Components of the Automotive Mechanic Training Process
The training process encompasses several core components designed to build comprehensive automotive knowledge. Engine mechanics forms a central part of the curriculum, covering combustion systems, fuel injection, and cooling mechanisms. Electrical systems training addresses wiring, battery management, and electronic control units that manage modern vehicle functions. Brake systems, suspension components, and transmission repair represent additional critical areas of study. Many programs also incorporate customer service skills and business practices, recognizing that mechanics often interact directly with vehicle owners and may eventually operate their own repair facilities.
Skills Development and Knowledge Acquisition in Automotive Mechanics
Skills development in automotive mechanic training emphasizes both technical proficiency and problem-solving abilities. Students practice diagnostic procedures using computerized equipment and traditional testing methods. Hands-on workshops allow trainees to work with actual vehicles, developing muscle memory and confidence in repair procedures. Communication skills receive attention as mechanics must explain complex technical issues to customers in understandable terms. Time management and efficiency become important as students learn to balance quality workmanship with productivity expectations common in commercial repair environments.
| Training Provider | Program Duration | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| City & Guilds | 1-3 years | £3,000-£8,000 |
| Pearson BTEC | 2-3 years | £4,000-£10,000 |
| Local Colleges | 1-2 years | £2,500-£6,000 |
| Private Training Schools | 6 months-2 years | £5,000-£12,000 |
| Apprenticeship Programs | 2-4 years | Employer-funded |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Training delivery methods vary significantly across different providers and program types. Traditional college courses offer structured learning environments with regular assessments and progression milestones. Apprenticeship programs combine paid work experience with formal education, allowing students to earn while learning practical skills in real workshop settings. Private training schools often provide intensive courses designed for career changers seeking rapid skill acquisition. Online components supplement practical training, covering theoretical knowledge and regulatory updates that affect automotive repair practices.
Certification and qualification pathways provide clear progression routes for automotive mechanic trainees. Level 2 qualifications establish foundational competency in basic vehicle maintenance and repair procedures. Level 3 certifications demonstrate advanced technical skills and diagnostic capabilities required for complex repair work. Specialized certifications in areas such as air conditioning, hybrid vehicles, or specific manufacturer systems enhance employment prospects and earning potential. Continuing professional development ensures mechanics stay current with evolving automotive technology and industry standards.
Career prospects for qualified automotive mechanics remain strong across the UK, with opportunities in independent garages, franchise dealerships, and specialized repair facilities. The transition toward electric and hybrid vehicles creates demand for mechanics with updated skills in battery systems and electric drivetrains. Geographic location influences employment opportunities, with urban areas typically offering more diverse career options while rural regions may provide opportunities for generalist mechanics serving broader communities. Professional development and specialization often lead to supervisory roles, workshop management positions, or independent business ownership.