Is Prostate Massage Safe? Potential Benefits Explained
Prostate massage is a technique that may be considered in the context of prostatitis treatment. This practice involves the stimulation of the prostate gland and is often discussed regarding its safety and potential therapeutic benefits. Understanding the implications of prostate massage is essential for individuals managing prostatitis, as it may provide relief from symptoms. This text explores the safety considerations, outlines potential benefits, and offers guidelines for engaging in prostate massage responsibly.
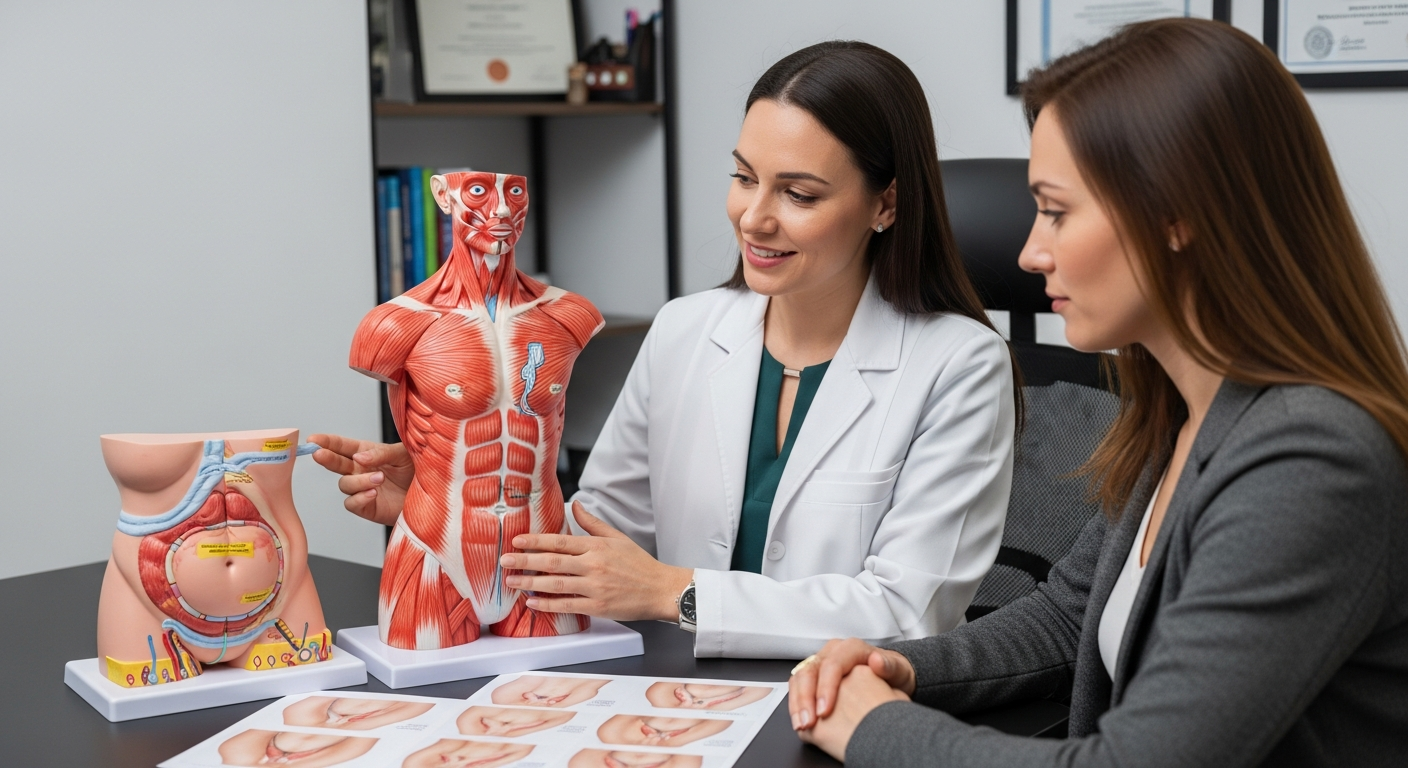

Prostate massage involves applying gentle pressure to the prostate gland, either externally through the perineum or internally through the rectum. This practice has been used historically in some medical settings and continues to be explored as a complementary approach for certain prostate conditions. The procedure aims to promote drainage of prostatic fluid and potentially reduce inflammation or discomfort associated with prostate issues.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding Prostate Massage and Its Safety Considerations
Prostate massage safety depends on several factors, including proper technique, hygiene practices, and individual health status. When performed correctly, the procedure generally carries minimal risk for most individuals. However, certain conditions may make prostate massage inadvisable. Acute bacterial prostatitis, for example, may worsen with massage due to the potential spread of infection. Similarly, individuals with prostate cancer, hemorrhoids, or anal fissures should avoid this technique.
Proper hygiene is essential to minimize infection risk. This includes thorough handwashing, using clean gloves, and applying appropriate lubricant. The massage should be gentle and never cause significant pain. If performed by a healthcare professional, sterile techniques and proper anatomical knowledge reduce potential complications. Self-administered massage requires careful research and understanding of anatomy to avoid injury.
Potential risks include rectal tissue damage, infection, exacerbation of existing conditions, and discomfort. These risks increase when the procedure is performed incorrectly or without proper preparation. Consulting with a healthcare provider before attempting prostate massage ensures that individual health factors are considered and that the technique is appropriate for specific circumstances.
Potential Benefits of Prostate Massage for Prostatitis Relief
Prostate massage has been explored as a potential therapeutic option for chronic prostatitis, particularly chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Some individuals report symptom improvement, including reduced pelvic discomfort, improved urinary flow, and decreased frequency of urination. The mechanism behind these benefits may involve promoting drainage of accumulated prostatic fluid, reducing inflammation, and improving blood circulation to the area.
Research on prostate massage effectiveness remains limited, with mixed results across studies. Some clinical observations suggest that regular massage sessions may help alleviate symptoms in certain cases of chronic non-bacterial prostatitis. However, the evidence is not conclusive enough to establish it as a standard treatment. Individual responses vary significantly, with some experiencing noticeable relief while others see minimal benefit.
Beyond prostatitis management, some practitioners suggest that prostate massage may support overall prostate health, though scientific validation for these broader claims is lacking. Any therapeutic approach should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan developed with medical guidance. Relying solely on prostate massage without addressing underlying causes or seeking proper diagnosis may delay appropriate medical intervention.
Guidelines for Practicing Safe Prostate Massage Techniques
Safe prostate massage requires proper preparation, technique, and awareness of anatomical structures. For those considering this approach, understanding correct methodology is crucial to minimize risks and maximize potential benefits. The procedure should always begin with thorough hygiene measures, including washing hands and the anal area, using disposable gloves, and applying generous amounts of water-based lubricant.
The prostate gland is located approximately two to three inches inside the rectum, toward the front of the body. It feels like a small, rounded bulge about the size of a walnut. Gentle pressure should be applied in a stroking or circular motion, never forcefully. Sessions typically last between one to three minutes and should never cause sharp pain. Mild pressure or slight discomfort may occur, but significant pain indicates improper technique or an underlying issue requiring medical attention.
For external massage, pressure is applied to the perineum, the area between the scrotum and anus. This approach is less invasive but may be less effective for reaching the prostate directly. Some individuals prefer starting with external techniques before progressing to internal methods. Regardless of approach, listening to body signals and stopping if discomfort increases is essential.
Professional administration by trained healthcare providers, such as urologists or specialized physical therapists, offers the safest option. These professionals understand proper anatomy, can assess individual suitability, and perform the technique with appropriate medical oversight. Self-administration or partner-assisted massage should only occur after thorough research and, ideally, initial guidance from a healthcare professional.
Frequency recommendations vary, but many sources suggest limiting sessions to once or twice weekly to avoid overstimulation or tissue irritation. Consistency matters more than frequency when seeking therapeutic benefits. Keeping a symptom diary can help track whether the practice provides noticeable relief or if alternative approaches should be considered.
When to Seek Professional Medical Guidance
While prostate massage may offer benefits for some individuals, it should never replace comprehensive medical evaluation and treatment. Anyone experiencing prostate-related symptoms, including pelvic pain, urinary difficulties, or sexual dysfunction, should consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis. These symptoms can indicate various conditions requiring different treatment approaches, from bacterial infections needing antibiotics to other urological issues.
Medical professionals can determine whether prostate massage is appropriate based on individual health status, symptom patterns, and diagnostic findings. They can also provide instruction on proper technique or perform the procedure in a clinical setting. Additionally, healthcare providers can recommend complementary treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, dietary modifications, or lifestyle changes that address underlying causes rather than just symptoms.
Signs that warrant immediate medical attention include fever accompanying pelvic pain, blood in urine or semen, severe or worsening symptoms, or inability to urinate. These may indicate serious conditions requiring prompt intervention. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures that any chosen treatment approach, including prostate massage, is monitored for effectiveness and safety over time.
Prostate massage remains a topic of ongoing discussion within medical communities. While some evidence and anecdotal reports suggest potential benefits for specific prostate conditions, particularly chronic prostatitis, the practice requires careful consideration of safety factors, proper technique, and individual health circumstances. Understanding both the potential advantages and limitations helps individuals make informed decisions in consultation with qualified healthcare professionals.