Medical Assistant Training Available for English Speakers in Madagascar
Residents of Madagascar who are proficient in English may be interested in medical assistant training. This program encompasses various aspects of healthcare support, including administrative tasks and patient care techniques. The training process is designed to equip participants with the necessary skills to excel in a medical environment.
Medical assistants play a vital role in healthcare facilities across Madagascar, supporting physicians, nurses, and other medical professionals in delivering patient care. As the country works to improve healthcare access and quality, the demand for trained medical assistants continues to grow. For English-speaking residents and international students, training programs designed to accommodate language needs provide a pathway into this rewarding field.
Understanding the Role and Responsibilities of a Medical Assistant
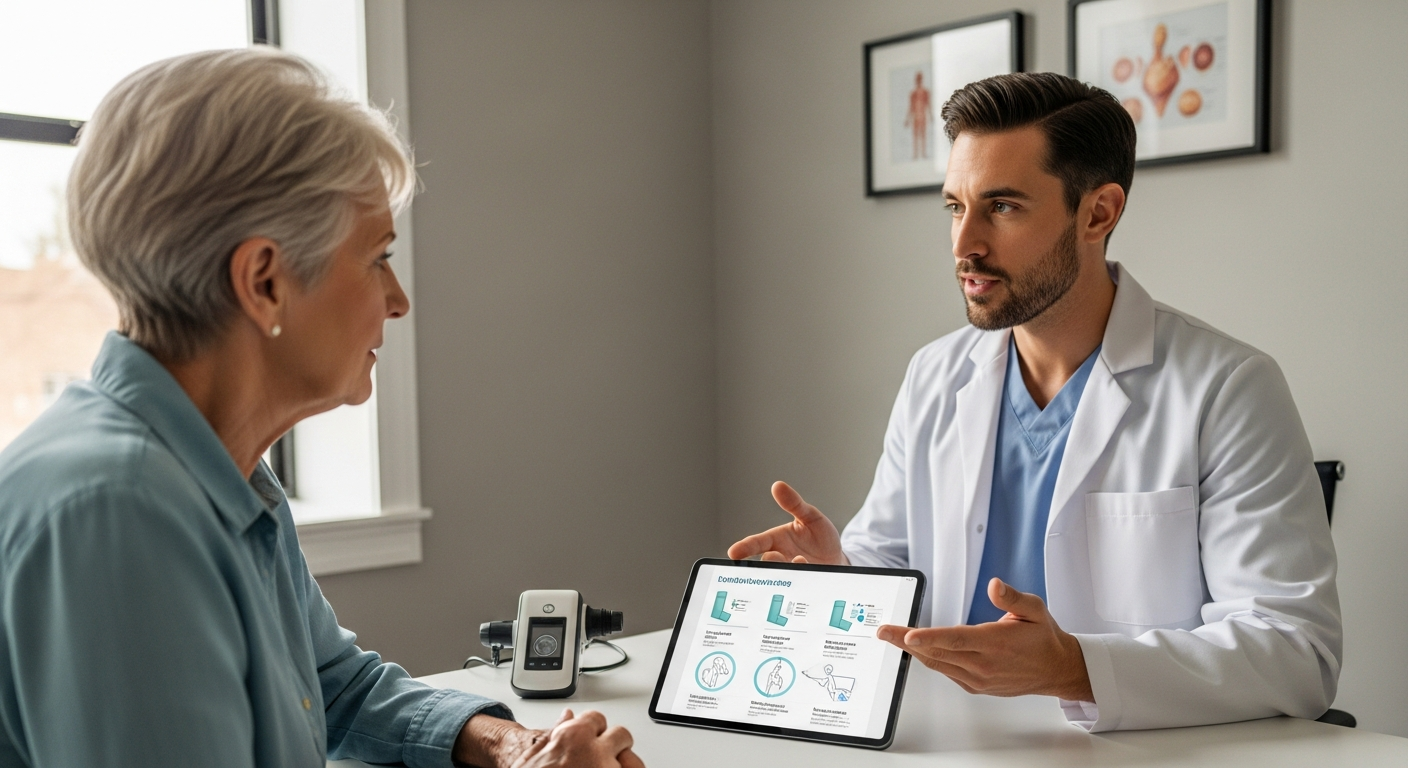
Medical assistants serve as essential support staff in hospitals, clinics, and private practices throughout Madagascar. Their responsibilities typically span both clinical and administrative domains. On the clinical side, medical assistants may take patient vital signs, prepare examination rooms, assist physicians during procedures, collect laboratory specimens, and administer medications under supervision. They often serve as the first point of contact for patients, helping to create a welcoming environment while gathering initial health information.
Administrative duties form another critical component of the role. Medical assistants frequently manage patient records, schedule appointments, handle billing and insurance documentation, and maintain medical supplies inventory. In Madagascar’s healthcare system, where resources may be limited and facilities serve diverse populations, medical assistants must be adaptable and capable of handling multiple tasks efficiently. The combination of clinical knowledge and organizational skills makes medical assistants invaluable team members in healthcare delivery.
For English speakers, the ability to communicate effectively with international patients, expatriate communities, and medical tourists adds significant value to their skill set. Madagascar’s growing medical tourism sector and presence of international organizations create specific opportunities for bilingual medical assistants who can navigate both local and global healthcare contexts.
Overview of the Medical Assistant Training Process in Madagascar
Medical assistant training in Madagascar typically involves structured educational programs that combine classroom instruction with hands-on clinical experience. Programs may vary in length, generally ranging from several months to two years, depending on the depth of training and certification level pursued. Coursework covers anatomy and physiology, medical terminology, pharmacology basics, infection control, patient care techniques, and healthcare documentation.
Training institutions in Madagascar may include vocational schools, technical colleges, and healthcare facilities offering apprenticeship-style programs. For English speakers, some institutions provide instruction in English or offer bilingual programs that accommodate non-French speakers while ensuring students can function effectively in Madagascar’s predominantly French and Malagasy-speaking healthcare environment. Practical training components allow students to apply their knowledge in real clinical settings, working alongside experienced healthcare professionals.
Certification requirements and standards continue to develop as Madagascar strengthens its healthcare workforce regulations. Students should verify that their chosen training program meets current national standards and provides recognized credentials that will be accepted by potential employers. Many programs also incorporate training in local health challenges, tropical medicine considerations, and community health approaches relevant to Madagascar’s specific healthcare needs.
Cost Considerations for Medical Assistant Training Programs
The financial investment required for medical assistant training in Madagascar varies based on program type, duration, and institution. Prospective students should research multiple options to understand the full cost structure. Training expenses typically include tuition fees, textbooks and learning materials, uniform and equipment costs, examination fees, and potential living expenses for students relocating to attend programs.
| Program Type | Institution Example | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term Certificate | Vocational Training Centers | $500 - $1,500 USD |
| Comprehensive Diploma | Technical Colleges | $1,500 - $4,000 USD |
| Extended Programs with Specialization | Private Healthcare Academies | $3,000 - $6,000 USD |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Some training institutions offer payment plans, scholarships, or financial assistance programs to help students manage costs. International organizations working in Madagascar’s healthcare sector occasionally provide funding or sponsored training opportunities. Students should inquire directly with training providers about available financial support options and verify what expenses are included in quoted program fees.
Importance of English Proficiency in Medical Assistant Training
English proficiency offers distinct advantages for medical assistants working in Madagascar’s healthcare system. While French and Malagasy remain the primary languages in most healthcare settings, English skills enable medical assistants to serve international patients, work with global health organizations, and access broader professional development resources. Many medical textbooks, research publications, and continuing education materials are available primarily in English, giving bilingual medical assistants enhanced learning opportunities.
Training programs designed for English speakers typically provide instruction in English while also teaching essential medical terminology in French and Malagasy. This trilingual approach prepares graduates to communicate effectively across different patient populations and work environments. Students learn to translate medical concepts between languages, ensuring accurate information exchange in clinical settings.
The presence of international NGOs, research institutions, and medical missions in Madagascar creates employment opportunities specifically seeking English-speaking medical assistants. These positions often offer competitive compensation and exposure to advanced medical practices. Additionally, English proficiency can facilitate career mobility, allowing medical assistants to pursue opportunities in other English-speaking African nations or international healthcare organizations operating across multiple countries.
Career Outlook and Professional Development
Completing medical assistant training opens diverse career pathways within Madagascar’s healthcare system. Graduates may find employment in urban hospitals, rural health centers, specialty clinics, pharmaceutical companies, public health programs, or private medical practices. The healthcare sector’s ongoing expansion, driven by population growth and improving infrastructure, suggests continued demand for qualified medical assistants.
Professional development opportunities allow medical assistants to advance their careers through specialized training in areas such as pediatrics, geriatrics, emergency care, or laboratory procedures. Some medical assistants use their initial training as a foundation for pursuing further education in nursing, healthcare administration, or other medical professions. Continuing education helps medical assistants stay current with evolving medical practices, technologies, and patient care standards.
Networking with healthcare professionals, joining professional associations, and participating in workshops or conferences can enhance career prospects. For English-speaking medical assistants, maintaining language skills and cultural competency proves valuable as Madagascar’s healthcare system becomes increasingly connected to global health initiatives and international medical standards.
Medical assistant training represents a practical entry point into Madagascar’s healthcare field, particularly for English speakers seeking meaningful work in a growing sector. By understanding the role’s requirements, training process, and importance of language skills, prospective students can pursue this career path with realistic expectations and appropriate preparation.




